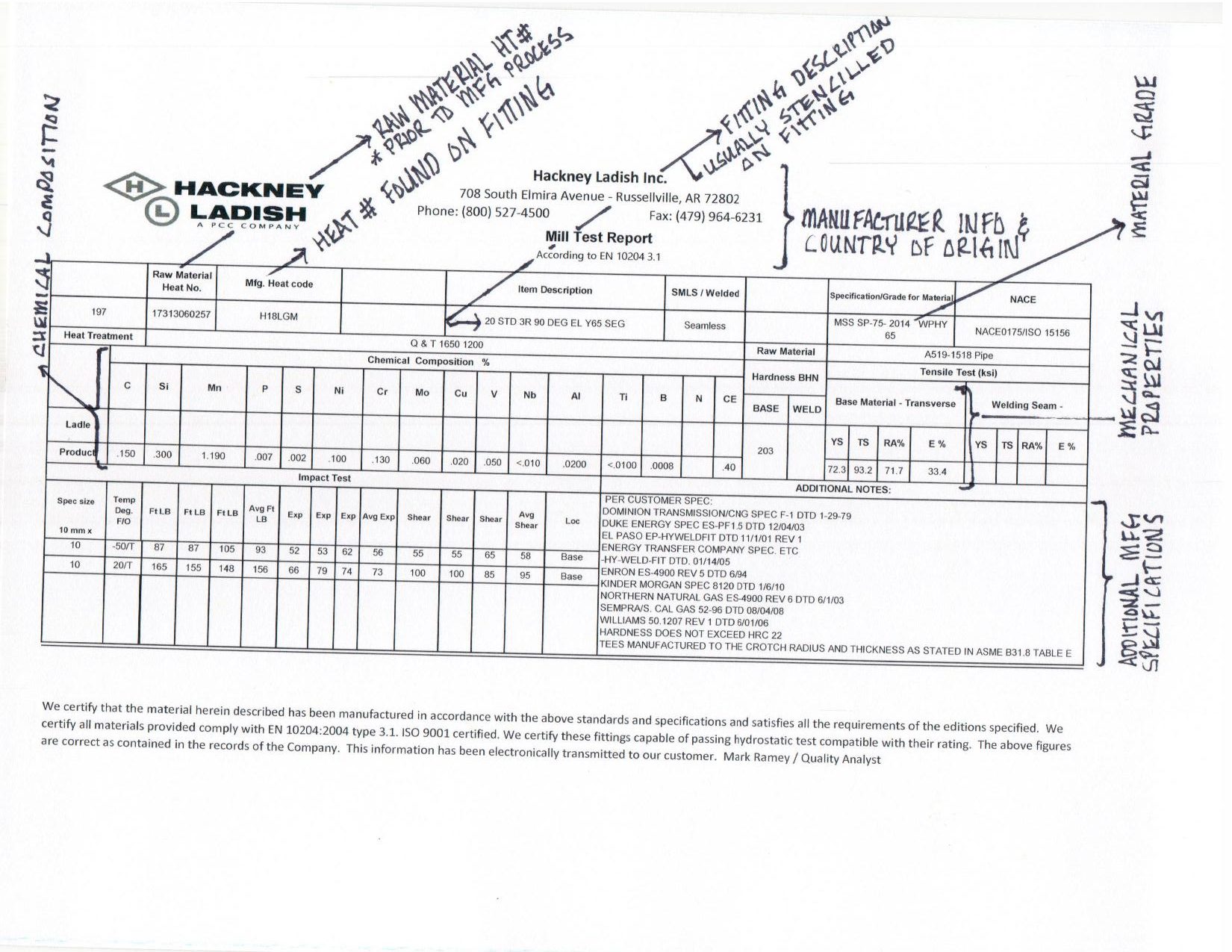
Material test reports are the primary guarantees of quality control in the pipe, valve, and fitting industry. Once you know how to read them, it becomes very easy to interpret the data they provide and understand what all that information means to you as a buyer of a steel product. To help you understand MTRs, BS Company has put together this list of definitive answers to all the most commonly asked questions about these documents.
What is a Material Test Report (MTR)?
A material test report (MTR), sometimes called a mill/manufacturer test report, is a certified record of a steel product’s physical and chemical propertiesand in some cases, raw material origins. These properties are measured against standards set up by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), in order to control and ensure quality. An MTR ensures proper compliance with these standards, and presents the buyer with documentary proof of that compliance.
What Information Does A Material Test Report (MTR) Contain?
The formats of MTRs are not necessarily uniform. Depending on the product, some MTRs will contain information that others do not. That being said, there are some general pieces of information that MTRs will contain in order to be useful to the person buying the product. These include:
- Material Heat Number
- Material Grade
- Edition Year and Type of Specifications Met
- Material Dimensions
- Mechanical Properties
- Chemical Analysis
- Heat Treatment (if applicable)
- Certified Inspector Signature
What Is A Heat Number/Heat code?
The heat number provides a traceable record of a piece of steel’s origin. By looking at the heat number, you can tell where the piece was forged. You can also use the number as a reference to find out valuable information about the steel’s composition. Having access to the heat number helps us to ensure the quality and reliability of steel components.
How Are Heat Codes/Heat Numbers Used?
Heat numbers are most often stenciled onto a piece of steel. Wherever that piece of steel is used, people can refer to that number and use it to trace the origins of the steel pipe, valve, or fitting. It is an assurance of quality and fidelity used at every point in the supply chain and placing the ultimate responsibility for the forged item at the feet of the original manufacturer.
What Is A Material Grade?
The material grade indicates the specific purpose for which a metal product has been produced, based on its mechanical and chemical properties.
What Are Mechanical Properties?
Mechanical properties are the physical attributes of the material, including its hardness, elasticity, tensile strength, elongation, hardness and fatigue limit.
What Is Chemical Analysis?
The chemical analysis on the MTR provides a complete qualitative and quantitative breakdown of the product’s chemical composition. The percentages of elements such as chromium, iron, etc., are stated on the MTR. The chemical composition tells us what purpose the piece is best used for. The analysis is carried out through various methods, including chromatography, gravimetric analysis, ICP analysis, OES analysis, SEM-EDS analysis and XRF analysis.
What Is Heat Treatment?
The term ‘heat treatment’ refers to any method used to alter the physical or chemical properties of steel by applying extreme temperatures (either heat or cold). Heat treatment methods include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering, carburizing, normalizing, and quenching.
Why Are Material Test Reports (MTRs) Important?
An MTR is essential to everyone who handles a steel product, from the original manufacturer to the end-user. A metal forge will need to include an MTR with all raw materials that it produces. The MTR provides proof that the forge complied with all the relevant standards when manufacturing that particular piece. Each stage that the steel then progresses to after the forge can then refer to the MTR to ensure that the materials they choose for their projects are up to standards. This reference system enables people at each stage of the process to secure and maintain standards of quality and safety.
How Do I Read A Material Test Report (MTR)?
Many people are intimidated by MTRs, but they are relatively easy to read if you just follow three straightforward steps:
- Step 1: First, inspect the material itself and reference the heat number stenciled or stamped on it against the heat number printed on the MTR. If they match, you know that the MTR you hold is the correct one for the material you’re inspecting.
- Step 2: Next, turn to the chemical analysis sections of the MTR. Check the measured quantities against the required percentage values to determine the quality of the material in light of ANSI or ASME standards.
- Step 3: Check the mechanical properties reported on the MTR and ensure that the tensile strength, hardness, Charpy impact test results, and yield strength are up to standard and appropriate for your purposes.
About BS Company
BS Company opened its doors in 1990 at a small 8,000 sq/ft location, “The Office” in Magna, UT. We’re grateful for the growth we’ve seen over the years and now operate three branches and one manufacturing facility. Our inventory consists of:
- 6,000 + tons of pipe ON THE GROUND! (300 semi truckloads)
- 1,500 + tons of fittings & flanges ON THE GROUND! (75 semi truckloads)
- 10,000 + valves ON THE GROUND
Our pipe and fitting inventory is held at our “Pipe Yard” in Toole, Utah. The “Pipe Yard” boasts much more than its name. There are 30 acres of carbon steel pipe, HDPE pipe, and large OD carbon steel fittings and flanges on the ground at this location. A new 10,000 sq.ft. warehouse stocked with large OD valves was added in 2014. We have pipe sizes up to 108”, fittings & flanges up to 48”, valves up to 36”, and stainless steel fittings & flanges, studs & nuts, and more on this site.
All of our flanges, pipes and valves comply with all applicable industry standards and are accompanied by material test reports. Contact us for more information.